Manufacturing industry needs to make and ship
Material Transport
Material handling operations traditionally consume about 25% of a factory’s workforce, occupy 55% of floor space, and account for 30–70% of the total cost of goods produced, showing how much internal transport can dominate costs and resources.
Background Manual Work
Let your team do what they are good at. Commonly, manufacture ring employees need to perform menial and labor intensive tasks which can be automated
Introduce our autonomous mobile robots
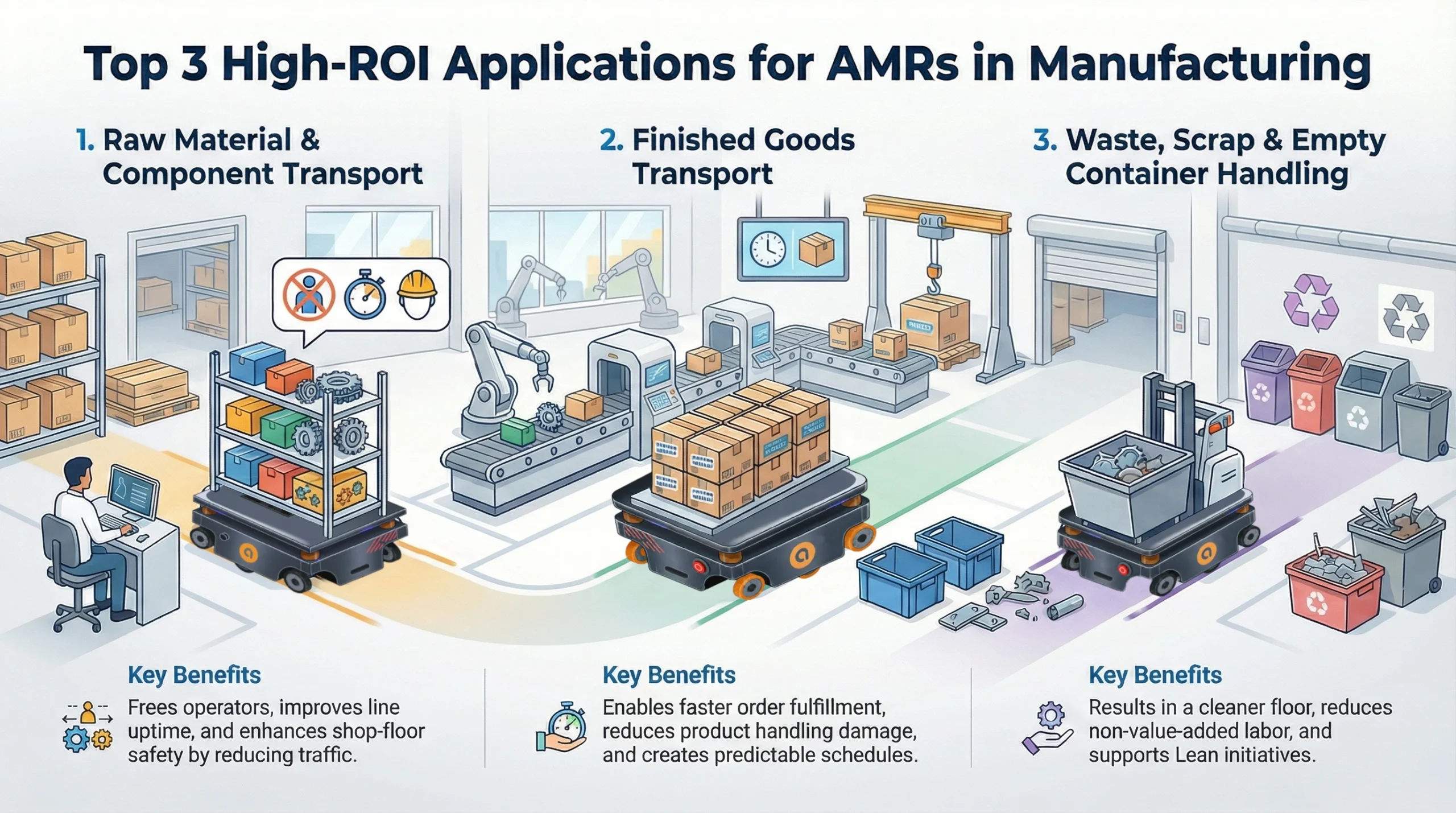
In a medium-sized manufacturing business (≈100–500 employees, single or multi-line facility), Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are most effective when applied to repetitive, high-frequency internal logistics tasks. The following three are the most common and highest-ROI candidates:
Material Transportation
AMRs move raw materials, components, and sub-assemblies from receiving or storage areas to production lines and between work cells.
Typical use cases
- Pallet, tote, or bin transport
- Line-side replenishment (just-in-time delivery)
- Inter-process movement in cellular manufacturing
Impact
- Frees operators from walking and driving tasks
- Improves line uptime and material availability
- Enhances shop-floor safety
Finished Goods Transport
AMRs transfer completed products from production lines to inspection, packaging, staging, and outbound docks.
Typical use cases
- Moving finished pallets to stretch-wrap stations
- Transporting cartons to quality inspection
- Dock staging for outbound shipping
Impact
- Faster order fulfillment
- Reduced product handling damage
- More predictable shipping schedules
Waste Handling
AMRs collect and return empty totes, pallets, bins, scrap metal, and packaging waste throughout the facility.
Typical use cases
- Returning empties to the warehouse
- Scrap removal from machining centers
- Cardboard and packaging waste transport
Impact
- Cleaner, safer shop floor
- Reduced non-value-added labor
- Better compliance with 5S / Lean initiatives